

История развития хранилищ для нефти: Первые склады нефти появились в XVII веке. Они представляли собой землянные ямы-амбара глубиной 4…5 м...

Кормораздатчик мобильный электрифицированный: схема и процесс работы устройства...

История развития хранилищ для нефти: Первые склады нефти появились в XVII веке. Они представляли собой землянные ямы-амбара глубиной 4…5 м...

Кормораздатчик мобильный электрифицированный: схема и процесс работы устройства...
Топ:
Теоретическая значимость работы: Описание теоретической значимости (ценности) результатов исследования должно присутствовать во введении...
История развития методов оптимизации: теорема Куна-Таккера, метод Лагранжа, роль выпуклости в оптимизации...
Интересное:
Искусственное повышение поверхности территории: Варианты искусственного повышения поверхности территории необходимо выбирать на основе анализа следующих характеристик защищаемой территории...
Что нужно делать при лейкемии: Прежде всего, необходимо выяснить, не страдаете ли вы каким-либо душевным недугом...
Берегоукрепление оползневых склонов: На прибрежных склонах основной причиной развития оползневых процессов является подмыв водами рек естественных склонов...
Дисциплины:
|
из
5.00
|
Заказать работу |
Содержание книги
Поиск на нашем сайте
|
|
|
|
Ø Turbojet

§ The turbojet engine consists of four sections: compressor, combustion chamber, turbine section, and exhaust. The compressor section passes inlet air at a high rate of speed to the combustion chamber
§ The combustion chamber contains the fuel inlet and igniter for combustion
§ The expanding air drives a turbine, which is connected by a shaft to the compressor, sustaining engine operation
§ The accelerated exhaust gases from the engine provide thrust
§ This is a basic application of compressing air, igniting the fuel-air mixture, producing power to self-sustain the engine operation, and exhaust for propulsion
§ Turbojet engines are limited in range and endurance
§ They are also slow to respond to throttle applications at slow compressor speeds
Ø Turboprop
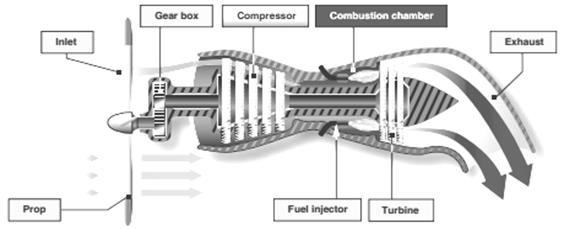
§ A turboprop engine is a turbine engine that drives a propeller through a reduction gear.
§ The exhaust gases drive a power turbine connected by a shaft that drives the reduction gear assembly
§ Reduction gearing is necessary in turboprop engines because optimum propeller performance is achieved at much slower speeds than the engine' operating rpm
§ Turboprop engines are a compromise between turbojet engines and reciprocating power plants
§ Turboprop engines are most efficient at speeds between 250 and 400 mph and altitudes between 18,000 and 30,000'
§ They also perform well at the slow airspeeds required for takeoff and landing, and are fuel efficient
§ The minimum specific fuel consumption of the turboprop engine is normally available in the altitude range of 25,000' to the tropopause.
Ø Turbofan

§ Turbofans were developed to combine some of the best features of the turbojet and the turboprop.
§ Turbofan engines are designed to create additional thrust by diverting a secondary airflow around the combustion chamber.
§ The turbofan bypass air generates increased thrust, cools the engine, and aids in exhaust noise suppression.
§ This provides turbojet-type cruise speed and lower fuel consumption.
§ The inlet air that passes through a turbofan engine is usually divided into two separate streams of air.
§ One stream passes through the engine core, while a second stream bypasses the engine core.
§ It is this bypass stream of air that is responsible for the term "bypass engine".
§ A turbofan's bypass ratio refers to the ratio of the mass airflow that passes through the fan divided by the mass airflow that passes through the engine core.
Ø Turboshaft

§ The fourth common type of jet engine is the turboshaft
§ It delivers power to a shaft that drives something other than a propeller
§ The biggest difference between a turbojet and turboshaft engine is that on a turboshaft engine, most of the energy produced by the expanding gases is used to drive a turbine rather than produce thrust
§ Many helicopters use a turboshaft gas turbine engine
§ In addition, turboshaft engines are widely used as auxiliary power units on large aircraft
Unit IV
|
|
|

Особенности сооружения опор в сложных условиях: Сооружение ВЛ в районах с суровыми климатическими и тяжелыми геологическими условиями...

Автоматическое растормаживание колес: Тормозные устройства колес предназначены для уменьшения длины пробега и улучшения маневрирования ВС при...

Опора деревянной одностоечной и способы укрепление угловых опор: Опоры ВЛ - конструкции, предназначенные для поддерживания проводов на необходимой высоте над землей, водой...

Типы оградительных сооружений в морском порту: По расположению оградительных сооружений в плане различают волноломы, обе оконечности...
© cyberpedia.su 2017-2025 - Не является автором материалов. Исключительное право сохранено за автором текста.
Если вы не хотите, чтобы данный материал был у нас на сайте, перейдите по ссылке: Нарушение авторских прав. Мы поможем в написании вашей работы!